The primitive basis and optimized basis functions are usually
assigned to atoms. Moreover, it is possible to assign basis functions
in any vacant region using an 'empty' atom. You will find the empty atom 'E'
in the database (http://www.openmx-square.org/).
Using the basis functions and pseudopotential, though
the pseudopotential is a flat zero potential, you can put
the basis functions at any place independently of atomic position.
The empty atom scheme enables us to treat a vacancy state and a nearly free
electron state on metal surfaces within the LCAO method. As an example,
a calculation of a F-center in NaCl with a Cl vacancy is shown in Fig. 3.
We see that the highest occupied state at ![]() point is the F-center state.
You can follow the calculation using NaCl_FC.dat in the directory 'work'.
The geometry optimization and molecular dynamics simulations are also supported
for the empty atom. So, the position of empty atoms can be optimized variationally.
point is the F-center state.
You can follow the calculation using NaCl_FC.dat in the directory 'work'.
The geometry optimization and molecular dynamics simulations are also supported
for the empty atom. So, the position of empty atoms can be optimized variationally.
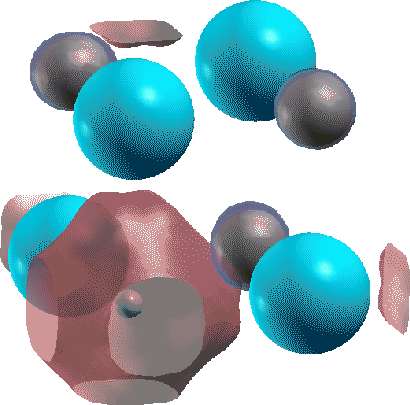 |